Integrate Kafka Connect Sources & Sinks¶
In the following getting started tutorial, we’ll focus on how to seamlessly integrate Kafka connect sources and sinks in logisland.
We can call this functionality Logisland connect.
Note
Be sure to know of to launch a logisland Docker environment by reading the prerequisites section
1. Logisland job setup¶
For this tutorial please make sure to already have installed elasticsearch and excel modules.
If not you can just do it through the components.sh command line:
bin/components.sh -i com.hurence.logisland:logisland-processor-elasticsearch:1.1.2
bin/components.sh -i com.hurence.logisland:logisland-service-elasticsearch_5_4_0-client:1.1.2
bin/components.sh -i com.github.jcustenborder.kafka.connect:kafka-connect-simulator:0.1.118
The logisland job for this tutorial is already packaged in the tar.gz assembly and you can find it here for ElasticSearch :
docker exec -i -t logisland vim conf/logisland-kafka-connect.yml
We will start by explaining each part of the config file.
The engine¶
The first section configures the Spark engine (we will use a KafkaStreamProcessingEngine) to run in local mode.
engine:
component: com.hurence.logisland.engine.spark.KafkaStreamProcessingEngine
type: engine
documentation: Use Kafka connectors with logisland
configuration:
spark.app.name: LogislandConnect
spark.master: local[2]
spark.driver.memory: 1G
spark.driver.cores: 1
spark.executor.memory: 2G
spark.executor.instances: 4
spark.executor.cores: 2
spark.yarn.queue: default
spark.yarn.maxAppAttempts: 4
spark.yarn.am.attemptFailuresValidityInterval: 1h
spark.yarn.max.executor.failures: 20
spark.yarn.executor.failuresValidityInterval: 1h
spark.task.maxFailures: 8
spark.serializer: org.apache.spark.serializer.KryoSerializer
spark.streaming.batchDuration: 1000
spark.streaming.backpressure.enabled: false
spark.streaming.unpersist: false
spark.streaming.blockInterval: 500
spark.streaming.kafka.maxRatePerPartition: 3000
spark.streaming.timeout: -1
spark.streaming.unpersist: false
spark.streaming.kafka.maxRetries: 3
spark.streaming.ui.retainedBatches: 200
spark.streaming.receiver.writeAheadLog.enable: false
spark.ui.port: 4050
The controllerServiceConfigurations part is here to define all services that be shared by processors within the whole job.
The parsing stream¶
Here we are going to use a special processor (KafkaConnectStructuredSourceProviderService) to use the kafka connect source as input for the structured stream defined below.
For this example, we are going to use the source com.github.jcustenborder.kafka.connect.simulator.SimulatorSourceConnector that generates records containing fake personal data at rate of 100 messages/s.
# Our source service
- controllerService: kc_source_service
component: com.hurence.logisland.stream.spark.provider.KafkaConnectStructuredSourceProviderService
documentation: A kafka source connector provider reading from its own source and providing structured streaming to the underlying layer
configuration:
# We will use the logisland record converter for both key and value
kc.data.value.converter: com.hurence.logisland.connect.converter.LogIslandRecordConverter
# Use kryo to serialize the inner data
kc.data.value.converter.properties: |
record.serializer=com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
kc.data.key.converter: com.hurence.logisland.connect.converter.LogIslandRecordConverter
# Use kryo to serialize the inner data
kc.data.key.converter.properties: |
record.serializer=com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
# Only one task to handle source input (unique)
kc.worker.tasks.max: 1
# The kafka source connector to wrap (here we're using a simulator source)
kc.connector.class: com.github.jcustenborder.kafka.connect.simulator.SimulatorSourceConnector
# The properties for the connector (as per connector documentation)
kc.connector.properties: |
key.schema.fields=email
topic=simulator
value.schema.fields=email,firstName,middleName,lastName,telephoneNumber,dateOfBirth
# We are using a standalone source for testing. We can store processed offsets in memory
kc.connector.offset.backing.store: memory
Note
The parameter kc.connector.properties contains the connector properties as you would have defined if you were using vanilla kafka connect.
As well, we are using a memory offset backing store. In a distributed scenario, you may have chosen a kafka topic based one.
Since each stream can be read and written, we are going to define as well a Kafka topic sink (KafkaStructuredStreamProviderService) that will be used as output for the structured stream defined below.
# Kafka sink configuration
- controllerService: kafka_out_service
component: com.hurence.logisland.stream.spark.structured.provider.KafkaStructuredStreamProviderService
configuration:
kafka.output.topics: logisland_raw
kafka.error.topics: logisland_errors
kafka.input.topics.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
kafka.output.topics.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
kafka.error.topics.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.JsonSerializer
kafka.metadata.broker.list: sandbox:9092
kafka.zookeeper.quorum: sandbox:2181
kafka.topic.autoCreate: true
kafka.topic.default.partitions: 4
kafka.topic.default.replicationFactor: 1
So that, we can now define the parsing stream using those source and sink
######### parsing stream ##############
- stream: parsing_stream_source
component: com.hurence.logisland.stream.spark.structured.StructuredStream
documentation: "Takes records from the kafka source and distributes related partitions over a kafka topic. Records are then handed off to the indexing stream"
configuration:
read.topics: /a/in
read.topics.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
read.topics.key.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
read.stream.service.provider: kc_source_service
write.topics: logisland_raw
write.topics.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
write.topics.key.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
write.stream.service.provider: kafka_out_service
Within this stream, a FlatMap processor takes out the value and key (required when using StructuredStream as source of records)
processorConfigurations:
- processor: flatten
component: com.hurence.logisland.processor.FlatMap
type: processor
documentation: "Takes out data from record_value"
configuration:
keep.root.record: false
copy.root.record.fields: true
The indexing stream¶
Inside this engine, you will run a Kafka stream of processing, so we set up input/output topics and Kafka/Zookeeper hosts.
Here the stream will read all the logs sent in logisland_raw topic and push the processing output into logisland_events topic.
Note
We want to specify an Avro output schema to validate our output records (and force their types accordingly). It’s really for other streams to rely on a schema when processing records from a topic.
We can define some serializers to marshall all records from and to a topic.
- stream: parsing_stream_source
component: com.hurence.logisland.stream.spark.structured.StructuredStream
documentation: "Takes records from the kafka source and distributes related partitions over a kafka topic. Records are then handed off to the indexing stream"
configuration:
read.topics: /a/in
read.topics.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
read.topics.key.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
read.stream.service.provider: kc_source_service
write.topics: logisland_raw
write.topics.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
write.topics.key.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
write.stream.service.provider: kafka_out_service
Within this stream, a DebugStream processor takes a log line as a String and computes a Record as a sequence of fields.
processorConfigurations:
# We just print the received records (but you may do something more interesting!)
- processor: stream_debugger
component: com.hurence.logisland.processor.DebugStream
type: processor
documentation: debug records
configuration:
event.serializer: json
This stream will process log entries as soon as they will be queued into logisland_raw Kafka topics, each log will be printed in the console and pushed back to Kafka in the logisland_events topic.
2. Launch the script¶
Connect a shell to your logisland container to launch the following streaming jobs.
docker exec -i -t logisland bin/logisland.sh --conf conf/logisland-kafka-connect.yml
3. Examine your console output¶
Since we put a DebugStream processor, messages produced by our source connectors are then output to the console in json.
18/04/06 11:17:06 INFO DebugStream: {
"id" : "9b17a9ac-97c4-44ef-9168-d298e8c53d42",
"type" : "kafka_connect",
"creationDate" : 1.4.106216376,
"fields" : {
"record_id" : "9b17a9ac-97c4-44ef-9168-d298e8c53d42",
"firstName" : "London",
"lastName" : "Marks",
"telephoneNumber" : "005-694-4540",
"record_key" : {
"email" : "londonmarks@fake.com"
},
"middleName" : "Anna",
"dateOfBirth" : 836179200000,
"record_time" : 1.4.106216376,
"record_type" : "kafka_connect",
"email" : "londonmarks@fake.com"
}
}
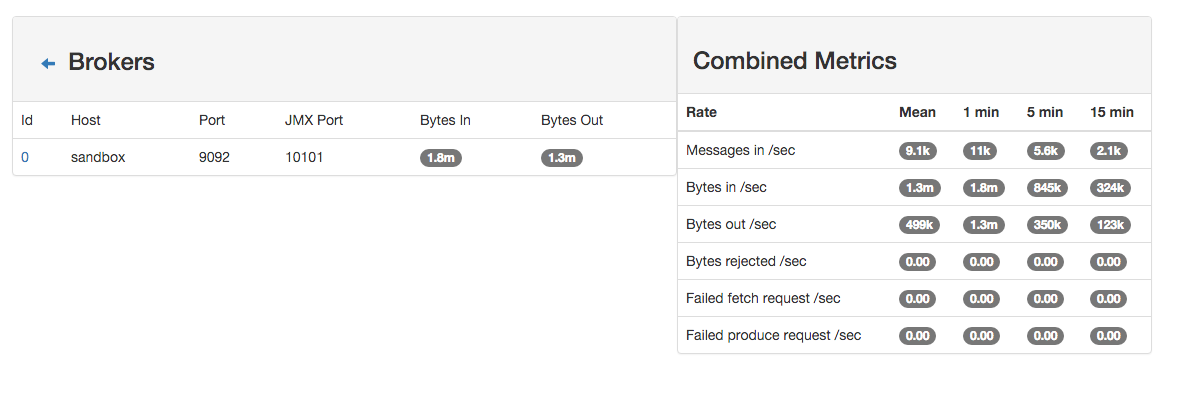
4. Monitor your spark jobs and Kafka topics¶
Now go to http://sandbox:4050/streaming/ to see how fast Spark can process your data
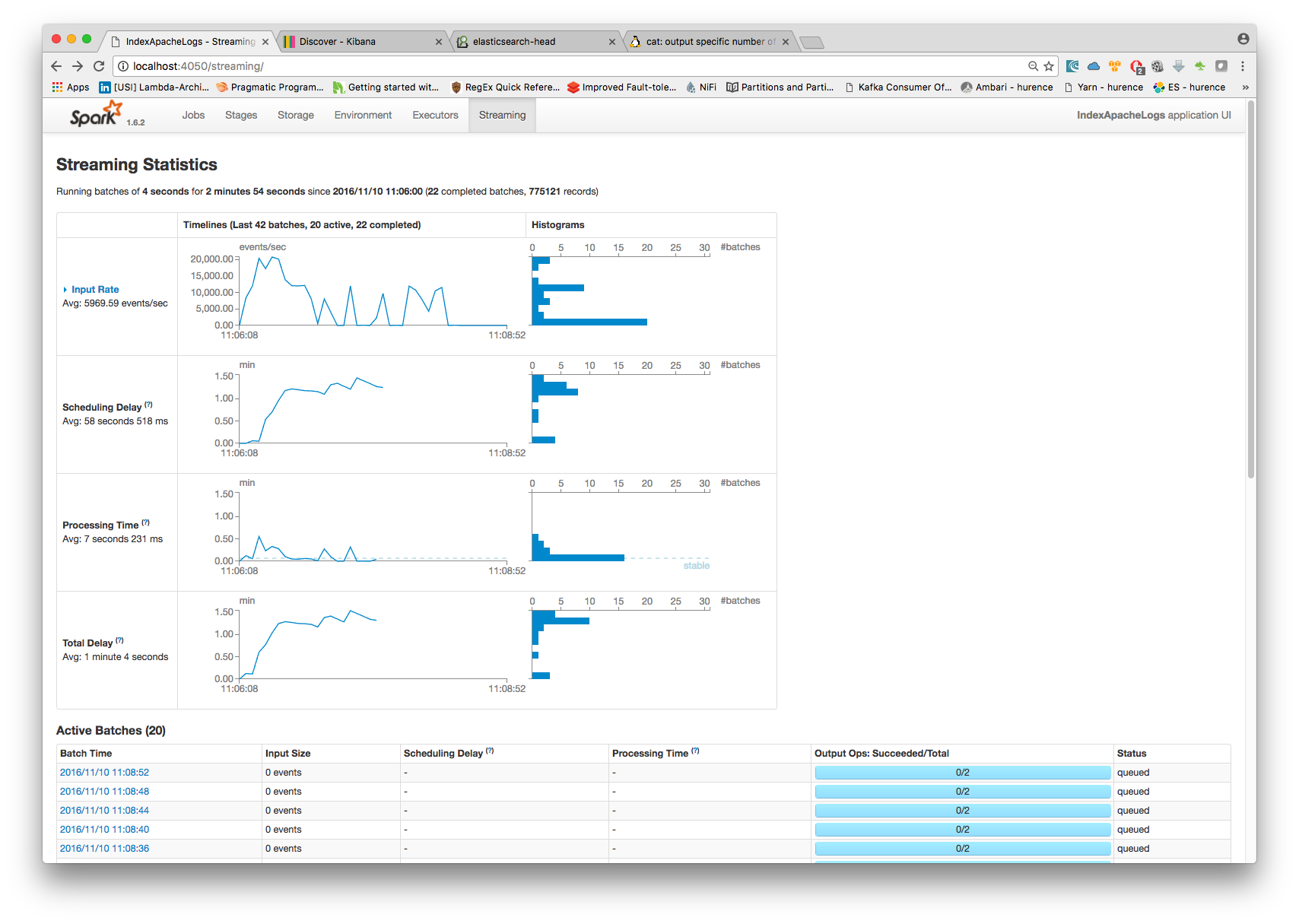
Another tool can help you to tweak and monitor your processing http://sandbox:9000/