Index blockchain transactions¶
In the following getting started tutorial, we’ll explain you how to leverage logisland connectors flexibility in order process in real time every transaction emitted by the bitcoin blockchain platform and index each record into an elasticsearch platform.
This will allow us to run some dashboarding and visual data analysis as well.
Note
Be sure to know of to launch a logisland Docker environment by reading the prerequisites section
For kafka connect related information please follow as well the connectors section.
1. Logisland job setup¶
Install the blockchain connector if not already done.
bin/components.sh -i com.datamountaineer:kafka-connect-blockchain:1.1.2
The logisland job for this tutorial is already packaged in the tar.gz assembly and you can find it here for ElasticSearch :
vim conf/index-blockchain-transactions.yml
We will start by explaining each part of the config file.
The engine¶
The first section configures the Spark engine (we will use a KafkaStreamProcessingEngine) to run in local mode.
engine:
component: com.hurence.logisland.engine.spark.KafkaStreamProcessingEngine
type: engine
documentation: Index some blockchain transactions with logisland
configuration:
spark.app.name: BlockchainTest
spark.master: local[*]
spark.driver.memory: 512M
spark.driver.cores: 1
spark.executor.memory: 512M
spark.executor.instances: 4
spark.executor.cores: 2
spark.yarn.queue: default
spark.yarn.maxAppAttempts: 4
spark.yarn.am.attemptFailuresValidityInterval: 1h
spark.yarn.max.executor.failures: 20
spark.yarn.executor.failuresValidityInterval: 1h
spark.task.maxFailures: 8
spark.serializer: org.apache.spark.serializer.KryoSerializer
spark.streaming.batchDuration: 2000
spark.streaming.backpressure.enabled: false
spark.streaming.blockInterval: 500
spark.streaming.kafka.maxRatePerPartition: 10000
spark.streaming.timeout: -1
spark.streaming.unpersist: false
spark.streaming.kafka.maxRetries: 3
spark.streaming.ui.retainedBatches: 200
spark.streaming.receiver.writeAheadLog.enable: false
spark.ui.port: 4040
The `controllerServiceConfigurations` part is here to define all services that be shared by processors within the whole job.
==================
The parsing stream
==================
Here we are going to use a special processor (``KafkaConnectStructuredSourceProviderService``) to use the kafka connect source as input for the structured stream defined below.
For this example, we are going to use the source *com.datamountaineer.streamreactor.connect.blockchain.source.BlockchainSourceConnector*
that opens a secure websocket connections to the blockchain subscribing to any transaction update stream.
.. code-block:: yaml
ControllerServiceConfigurations:
- controllerService: kc_source_service
component: com.hurence.logisland.stream.spark.provider.KafkaConnectStructuredSourceProviderService
configuration:
kc.data.value.converter: com.hurence.logisland.connect.converter.LogIslandRecordConverter
kc.data.value.converter.properties: |
record.serializer=com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
kc.data.key.converter.properties: |
schemas.enable=false
kc.data.key.converter: org.apache.kafka.connect.storage.StringConverter
kc.worker.tasks.max: 1
kc.connector.class: com.datamountaineer.streamreactor.connect.blockchain.source.BlockchainSourceConnector
kc.connector.offset.backing.store: memory
kc.connector.properties: |
connect.blockchain.source.url=wss://ws.blockchain.info/inv
connect.blockchain.source.kafka.topic=blockchain
Note
Our source is providing structured value hence we convert with LogInslandRecordConverter serializing with Kryo
# Kafka sink configuration
- controllerService: kafka_out_service
component: com.hurence.logisland.stream.spark.structured.provider.KafkaStructuredStreamProviderService
configuration:
kafka.output.topics: logisland_raw
kafka.error.topics: logisland_errors
kafka.input.topics.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
kafka.output.topics.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
kafka.error.topics.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.JsonSerializer
kafka.metadata.broker.list: sandbox:9092
kafka.zookeeper.quorum: sandbox:2181
kafka.topic.autoCreate: true
kafka.topic.default.partitions: 4
kafka.topic.default.replicationFactor: 1
So that, we can now define the parsing stream using those source and sink
######### parsing stream ##############
- stream: parsing_stream_source
component: com.hurence.logisland.stream.spark.structured.StructuredStream
documentation: "Takes records from the kafka source and distributes related partitions over a kafka topic. Records are then handed off to the indexing stream"
configuration:
read.topics: /a/in
read.topics.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
read.topics.key.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
read.stream.service.provider: kc_source_service
write.topics: logisland_raw
write.topics.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
write.topics.key.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
write.stream.service.provider: kafka_out_service
Within this stream, a FlatMap processor takes out the value and key (required when using StructuredStream as source of records)
processorConfigurations:
- processor: flatten
component: com.hurence.logisland.processor.FlatMap
type: processor
documentation: "Takes out data from record_value"
configuration:
keep.root.record: false
copy.root.record.fields: true
The indexing stream¶
Inside this engine, you will run a Kafka stream of processing, so we set up input/output topics and Kafka/Zookeeper hosts.
Here the stream will read all the logs sent in logisland_raw topic and push the processing output into logisland_events topic.
Note
We want to specify an Avro output schema to validate our output records (and force their types accordingly). It’s really for other streams to rely on a schema when processing records from a topic.
We can define some serializers to marshall all records from and to a topic.
- stream: parsing_stream_source
component: com.hurence.logisland.stream.spark.structured.StructuredStream
documentation: "Takes records from the kafka source and distributes related partitions over a kafka topic. Records are then handed off to the indexing stream"
configuration:
read.topics: /a/in
read.topics.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
read.topics.key.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
read.stream.service.provider: kc_source_service
write.topics: logisland_raw
write.topics.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
write.topics.key.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.KryoSerializer
write.stream.service.provider: kafka_out_service
Within this stream, a BulkAddElasticsearch takes care of indexing a Record sending it to elasticsearch.
- processor: es_publisher
component: com.hurence.logisland.processor.elasticsearch.BulkAddElasticsearch
type: processor
documentation: a processor that indexes processed events in elasticsearch
configuration:
elasticsearch.client.service: elasticsearch_service
default.index: logisland
default.type: event
timebased.index: yesterday
es.index.field: search_index
es.type.field: record_type
In details, this processor makes use of a Elasticsearch_5_4_0_ClientService controller service to interact with our Elasticsearch 5.X backend
running locally (and started as part of the docker compose configuration we mentioned above).
Here below its configuration:
- controllerService: elasticsearch_service
component: com.hurence.logisland.service.elasticsearch.Elasticsearch_5_4_0_ClientService
type: service
documentation: elasticsearch service
configuration:
hosts: sandbox:9300
cluster.name: es-logisland
batch.size: 5000
2. Launch the script¶
Connect a shell to your logisland container to launch the following streaming jobs.
bin/logisland.sh --conf conf/index-blockchain-transactions.yml
3. Do some insights and visualizations¶
With ElasticSearch, you can use Kibana.
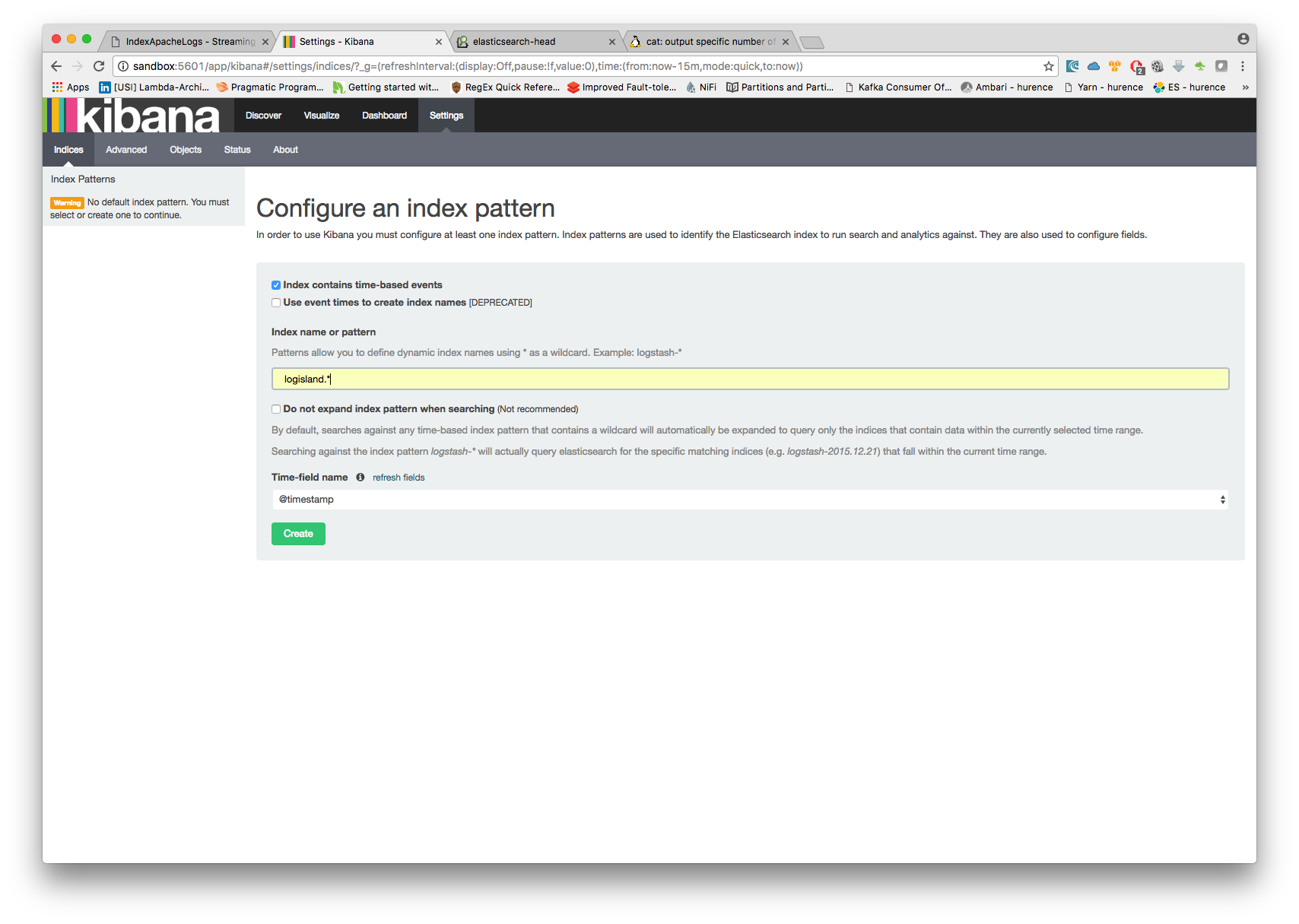
Open up your browser and go to http://sandbox:5601/app/kibana#/ and you should be able to explore the blockchain transactions.
Configure a new index pattern with logisland.* as the pattern name and @timestamp as the time value field.
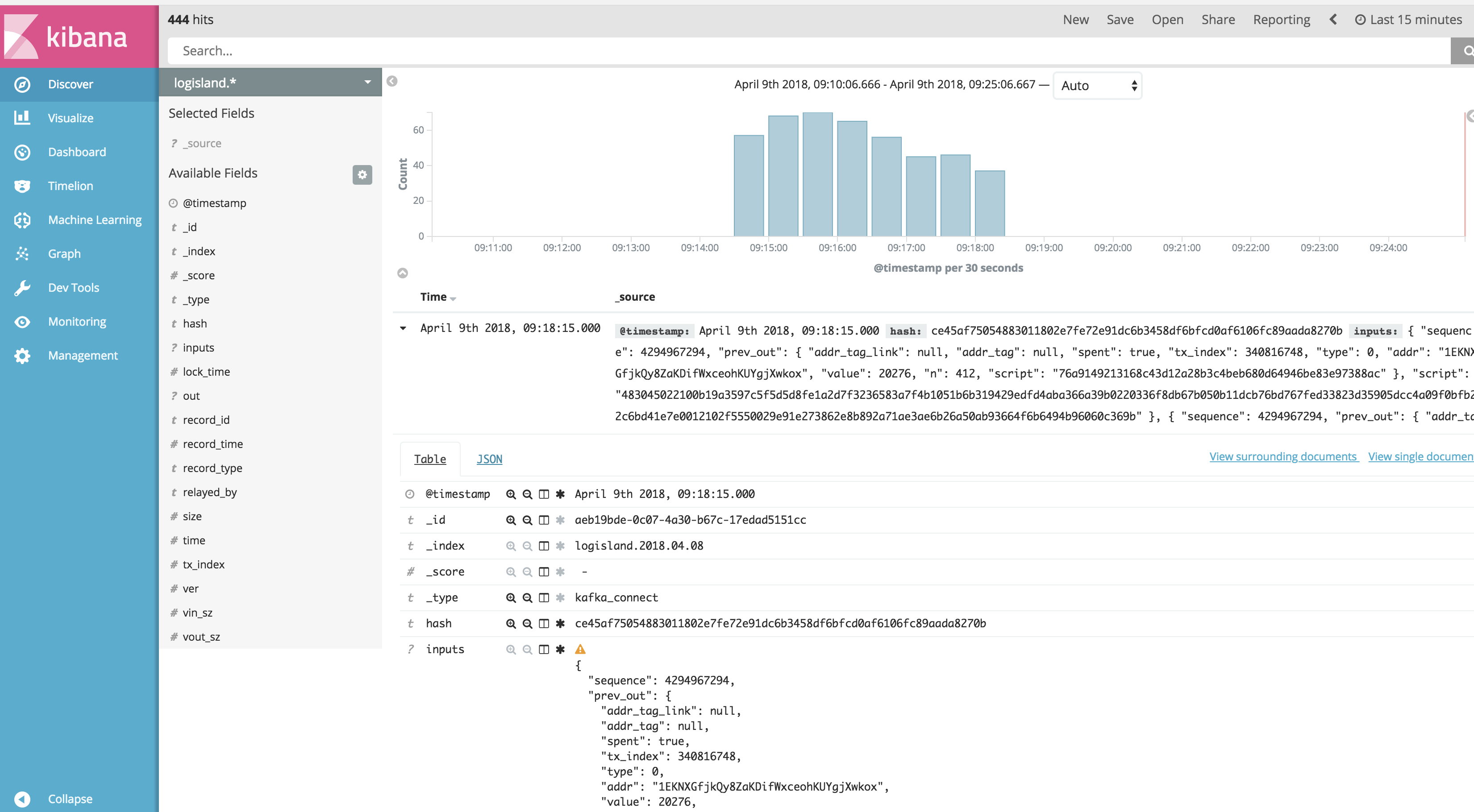
Then if you go to Explore panel for the latest 15’ time window you’ll only see logisland process_metrics events which give you insights about the processing bandwidth of your streams.
You can try as well to create some basic visualization in order to draw the total satoshi transacted amount (aggregating sums of out.value field).
Below a nice example:
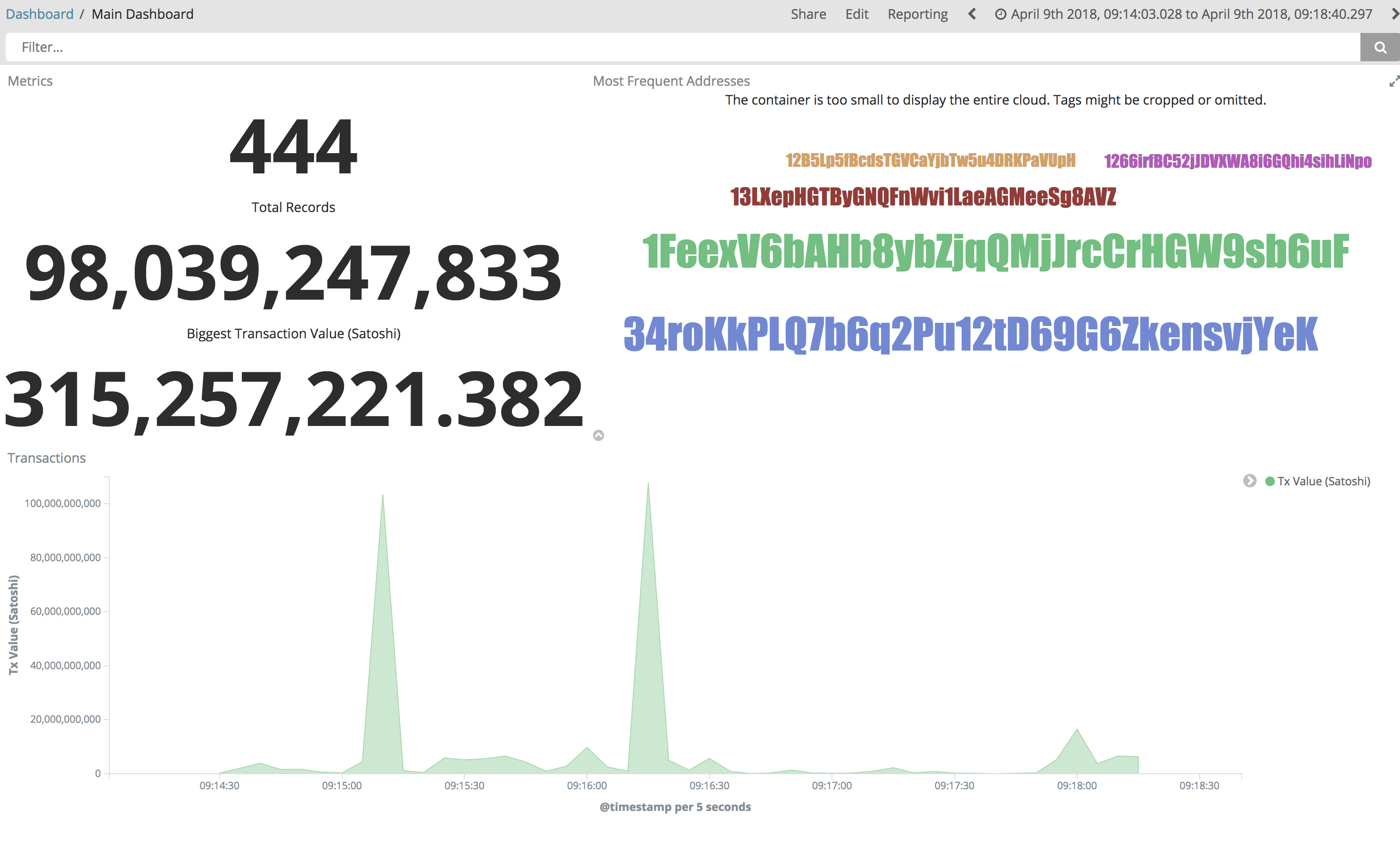
Ready to discover which addresses received most of the money? Give it a try ;-)
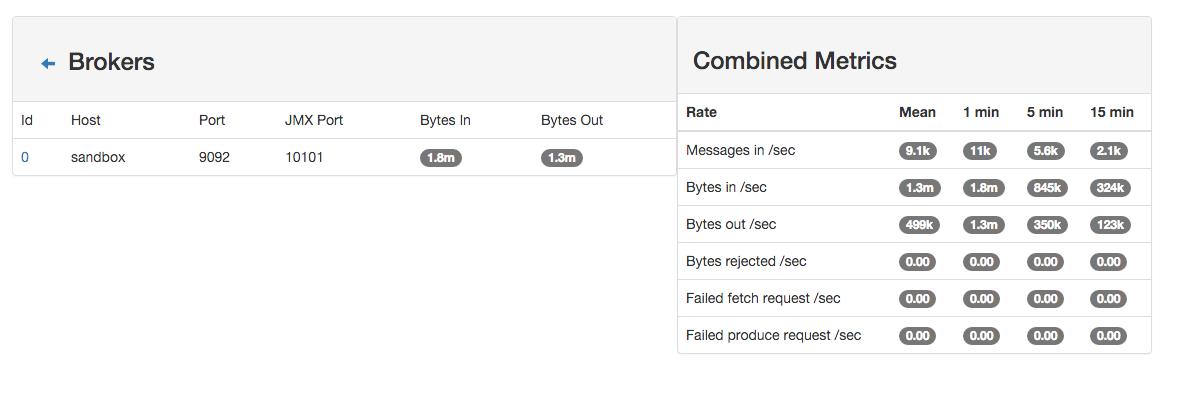
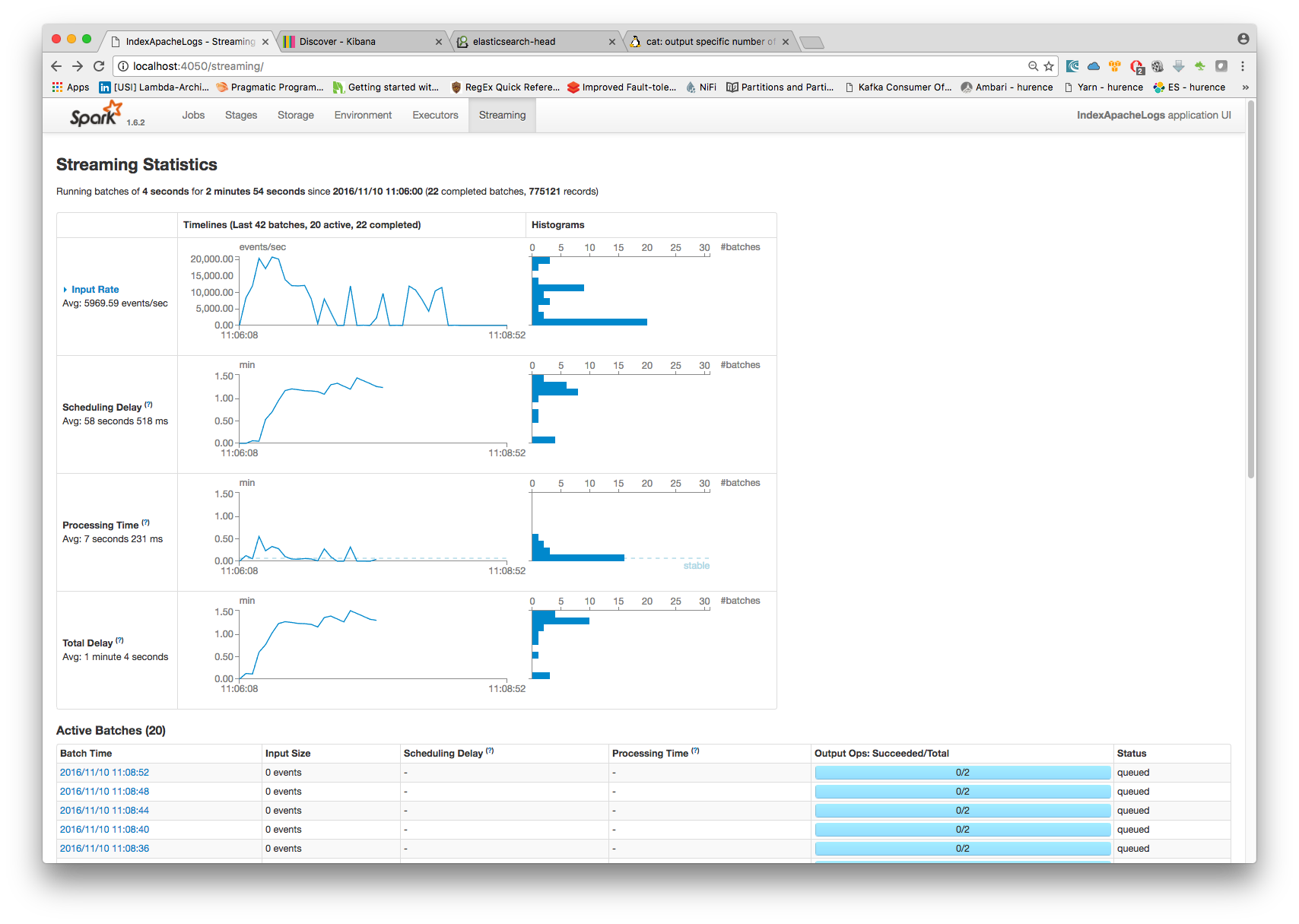
4. Monitor your spark jobs and Kafka topics¶
Now go to http://sandbox:4050/streaming/ to see how fast Spark can process your data
Another tool can help you to tweak and monitor your processing http://sandbox:9000/